What is the energy consumption of the fan under high-temperature and low-temperature conditions?
(1) Fan Energy Consumption in High-Temperature Environments
In high-temperature environments (>50°C), the power consumption of fans may increase due to the following factors:
- Increased motor resistance: As temperatures rise, the electrical resistance of wires and electronic components increases, requiring the fan to consume more energy to maintain its operational speed.
- Thinning of bearing lubricating oil: The viscosity of lubricating oil decreases at elevated temperatures, leading to increased bearing wear and potentially higher friction losses.
- Fan speed compensation: To preserve heat dissipation efficiency, many fans automatically increase their rotational speed in high-temperature conditions, which directly results in higher power consumption.
✅Example: Comparison of power consumption between a standard fan and a temperature-resistant fan in a high-temperature environment.

✅Conclusion: The power consumption of conventional fans rises significantly at high temperatures, whereas the power consumption of temperature-resistant fans remains more stable as a result of optimized motor and bearing designs.
(2) Fan Energy Consumption in Low-Temperature Environments
In low-temperature environments (<0°C), fan energy consumption may be influenced by the following factors:
• Increased Viscosity of Bearing Lubricating Oil: As temperature decreases, the viscosity of lubricating oil rises, leading to higher bearing friction and subsequently increased energy consumption of the fan.
• Material Contraction Effect: Certain plastic or metal components of the fan may contract at low temperatures, potentially disrupting smooth operation and increasing power consumption.
• Elevated Starting Current: At low temperatures, some fans require a higher starting current to overcome issues such as lubricating oil thickening and increased bearing friction during startup.
✅ Example: Comparison of Power Consumption Between a Standard Fan and a Temperature-Resistant Fan in Low-Temperature Conditions

✅Conclusion: Conventional fans are prone to issues such as the thickening of lubricating oil and increased starting resistance in low-temperature environments, which can lead to higher energy consumption. In contrast, temperature-resistant fans employ specialized bearings and low-temperature lubricants, thereby maintaining more stable energy efficiency.
2. How to Select a Low-Energy Fan? When selecting a temperature-resistant fan, you can consider the following aspects to reduce energy consumption and enhance the efficiency of the fan:
1。It is recommended to select a fan with a wide operating temperature range. Specifically, fans with an operating range of **-40°C to 85°C** are preferred. Suitable options include:
✔ Temperature-resistant fans (ideal for industrial applications, communication equipment, and photovoltaic inverters)
✔ Industrial-grade fans (suited for new energy vehicles, charging stations, and server systems)
(2) Select high-efficiency motors and optimize fan design.
✔ High-temperature windings: Reduce resistance losses at high temperatures to enhance motor efficiency.
✔ Low-temperature lubricated bearings: Ensure smooth operation in low-temperature environments while minimizing friction-related energy consumption.
(3) Emphasize the lifespan of the fan and minimize replacement costs. At both high and low temperatures, the lifespan of conventional fans is significantly compromised, whereas temperature-resistant fans can sustain stable energy consumption over an extended period, thereby reducing replacement and maintenance expenses.
✅ Example:Comparison of Fan Lifespan at Elevated Temperatures
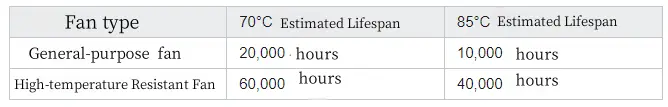
✅ Conclusion: The use of temperature resistant fans can reduce the frequency of maintenance and replacement, and reduce long-term energy costs.
Recommended scheme
✅ Communication equipment: Wide temperature range fan, improve long-term stability
✅ Photovoltaic inverter: industrial grade fan to reduce energy loss at high temperatures
✅ Charging pile: high temperature fan to ensure continuous heat dissipation and improve charging efficiency










