How does a cooling fan equipped with an integrated temperature sensor "detect" temperature?
The Cooling Fan equipped with an internal temperature sensor not only provides standard cooling functionality but also integrates temperature sensing and feedback capabilities. Its primary functions are as follows:
1️ Real-time Temperature Monitoring
Through the integrated temperature sensor, the fan can continuously monitor temperature fluctuations in the working environment. For example, when the equipment or surrounding environment experiences a rise in temperature, the fan will automatically activate or increase its rotational speed to maintain an optimal operating temperature.
2️ Automatic Fan Speed Adjustment
The built-in temperature sensor collaborates with the fan's PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) speed control mechanism, enabling the fan to dynamically adjust its rotational speed based on temperature variations. During periods of high temperature, the fan accelerates its operation, while during cooler conditions, it decelerates or halts operation entirely to conserve energy.
3️ Abnormal Temperature Alarm
Certain fans with integrated temperature sensors are capable of monitoring whether the device's temperature exceeds predefined thresholds. In the event of abnormal temperature increases, the fan will issue an alarm signal to prompt the system to implement emergency measures.
The working principle of the built-in temperature sensor involves several common temperature measurement methods. Typically, built-in temperature sensors utilize the following principles:
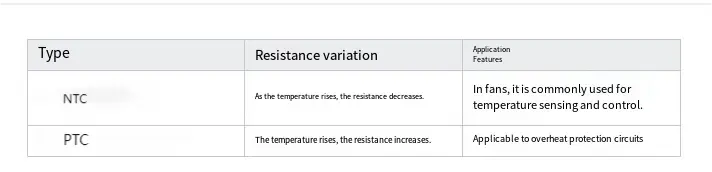
1. Thermistor (NTC/PTC).
A thermistor is a component whose resistance value varies with temperature changes. Specifically, the resistance of NTC (negative temperature coefficient) thermistors decreases as the temperature increases, whereas the resistance of PTC (positive temperature coefficient) thermistors increases with rising temperature.
2. Semiconductor Temperature Sensor
Semiconductor temperature sensors leverage the inherent thermal sensitivity of semiconductor materials. As the temperature varies, the resulting changes in current or voltage can be measured. These sensors are characterized by high precision and are commonly employed in applications demanding accurate temperature perception.
3. Thermocouple
A thermocouple determines temperature by measuring the thermal electromotive force (EMF) generated at the junctions of two dissimilar metals. Key advantages of thermocouples include their rapid response time and extensive measurement range, rendering them ideal for scenarios requiring real-time monitoring of temperature fluctuations.
There is typically a direct correlation between the rotational speed of a fan and its associated temperature.
The integrated temperature sensor collaborates with the fan's PWM speed control system to intelligently adjust the fan speed in response to temperature variations.

1️ At low temperatures,
When the equipment temperature is below a predefined threshold, the temperature sensor detects the signal and adjusts the fan speed to a minimal level or halts its operation entirely. This energy-saving mode not only extends the service life of the fan but also reduces unnecessary energy consumption.
2️ At medium temperatures,
When the equipment operates within its normal temperature range, the temperature sensor provides an appropriate feedback signal, allowing the fan to maintain a stable rotational speed for optimal heat dissipation.
3️ At high temperatures,
If the temperature sensor detects that the equipment has exceeded its safe operating limit, the fan accelerates its operation, increasing its rotational speed to rapidly expel excess heat and prevent potential malfunctions caused by overheating.
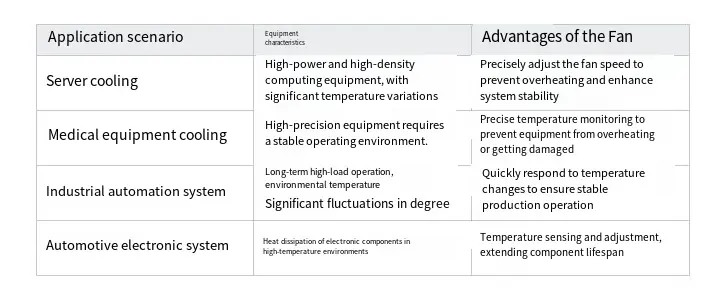
Application Scenarios and Technical Advantages:
Cooling fans equipped with built-in temperature sensors are extensively utilized in devices that demand precise temperature control. Specific application scenarios encompass the following areas:
Maintenance and Precautions for Temperature Sensor Fans
To ensure the long-term stable operation of cooling fans with built-in temperature sensors in practical applications, the following professional maintenance recommendations are provided:
1. Regular Cleaning
The heat dissipation efficiency of a fan is directly influenced by the cleanliness of its ventilation openings. It is essential to periodically remove dust and debris to maintain unobstructed airflow.
2. Temperature Sensor Calibration
Over time, the temperature sensor may exhibit certain deviations. Regular calibration should be performed to ensure that the sensor accurately detects the device's temperature.
3. Circuit Connection Inspection
It is critical to verify the stability of the connection between the fan and the motherboard or control system to prevent inaccurate temperature feedback caused by poor contact.
4. Selection of Suitable Fans
Choose an appropriate fan based on the heat dissipation requirements of the equipment. For example, high-performance cooling fans supplied by Shenzhen Fuqingda Electronic Technology Co., Ltd., are capable of precisely sensing temperature changes and providing highly efficient heat dissipation solutions.
Conclusion:
The integrated temperature sensor enables the cooling fan to not only perform traditional cooling functions but also accurately detect and respond to temperature fluctuations, thereby providing advanced intelligent temperature control.
This smart regulation enhances equipment stability while effectively extending the service life of both the fan and the device. Shenzhen Fuqingda Electronic Technology Co., Ltd. provides a wide range of cooling fans equipped with built-in temperature sensors, suitable for diverse and complex application scenarios. For more information regarding our intelligent temperature-controlLed Fans, please do not hesitate to contact us at your convenience.










