Could the wear of the cooling fan's bearings potentially lead to an increase in the sound pressure level?
I. The Role of Bearings in Cooling Fans
The primary functions of bearings in cooling fans are as follows:
• Support the high-speed rotation of the fan shaft;
• Minimize mechanical friction to ensure smooth and silent operation;
• Prolong the lifespan of the fan while enhancing operational efficiency.
Common types of bearings include:
• Sleeve Bearing: Featuring a simple structure and low cost, it is ideal for low-load and short-cycle applications;
• Ball Bearing: Characterized by a long service life and high stability, it is suitable for high-temperature and continuous-operation equipment;
• FDB/Magnetic Levitation/Hydrodynamic Bearings: Commonly employed in high-end silent products, these bearings combine quietness with an extended service life.
2. How does bearing wear lead to an increase in sound pressure level? When a bearing wears, the following phenomena occur: 
Note: The human ear can distinctly perceive a change of 3 dB(A). If the sound pressure level suddenly increases by more than 5 dB(A), it is highly probable that this is attributable to bearing issues.
3. How to Determine Noise Caused by Bearing Wear? The following methods can be employed for rapid troubleshooting:
• Sound inspection: Check if there are sharp abnormal noises or rhythmic "clicking" sounds during operation.
• Performance comparison: Observe whether the airflow has decreased, the sound pressure level has increased, while the rotational speed remains within the normal range.
• Bearings in fans that have been in continuous operation for over 1 to 2 years should be inspected with particular attention.
• Shaking test: When the fan blades are gently shaken manually, a "loose feeling" indicates bearing eccentricity.
4. What are the strategies to mitigate the increase in sound pressure level resulting from bearing wear?
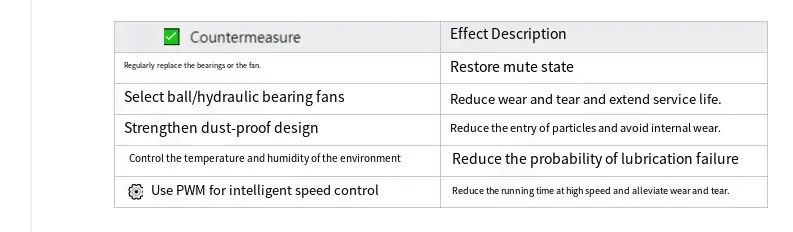
Conclusion:
Despite its small size, the bearing can generate considerable noise.
The acoustic performance of a cooling fan is influenced not only by parameters such as air volume and air pressure but also by the quality and wear condition of the bearings. Once the bearing becomes worn, it not only compromises heat dissipation efficiency but also substantially increases the sound pressure level, thereby impairing the quiet operation of the equipment.










