Can the FG (Fan Guard) signal output of the cooling fan be utilized for intelligent diagnostics?
What is the FG signal? What diagnostic information can it provide? The FG signal serves as a rotational speed feedback signal, typically output in pulse form. The output frequency is directly proportional to the actual rotational speed (RPM) of the Fan. It commonly operates at 2 PPR (two pulses per revolution) or 4 PPR.
Key characteristics of FG signal output include the following:
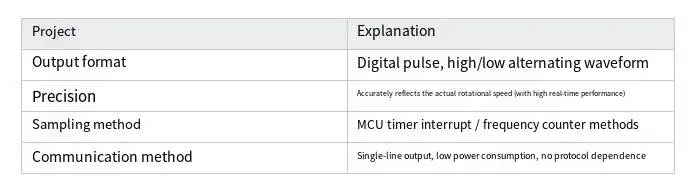
✅Essentially, the FG signal serves as a stable time-series data source, enabling the sampling and analysis of the following key diagnostic dimensions.
Which "intelligent diagnoses" can FG signals be used for?
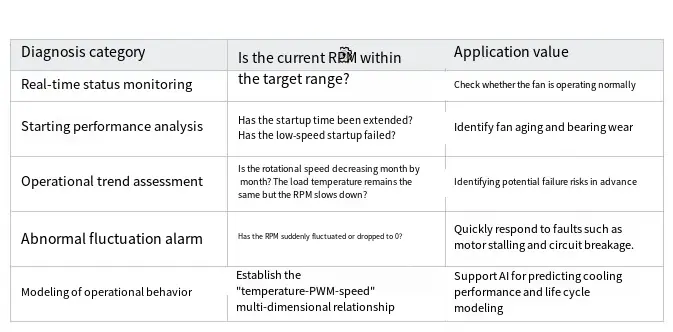
Example: How can we achieve intelligent diagnostic analysis utilizing FG signals?
Understand the Fan 'Health Curve' in One Minute: Suppose we record the fan RPM every 30 seconds and plot the curve for the past 24 hours.
- Normal Curve: The RPM fluctuates synchronously with temperature changes.
- Abnormal Trend: At a constant temperature, the RPM gradually decreases.
- Fault Diagnosis: The fan power supply is functioning normally, PWM is set at 70%, but RPM is 0 (indicating locked rotation or motor failure).
By integrating these trends into system monitoring, the host can achieve self-diagnostic capabilities and enable predictive maintenance of the fan status.
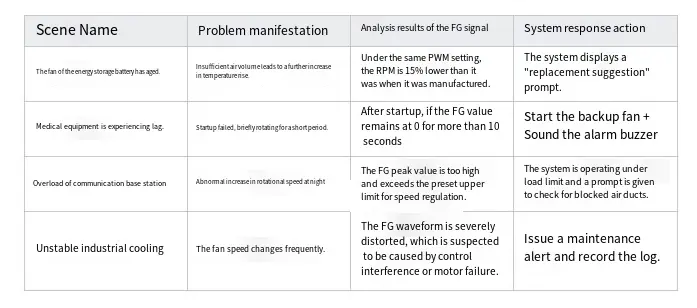
Intelligent Diagnostic Scenario Example
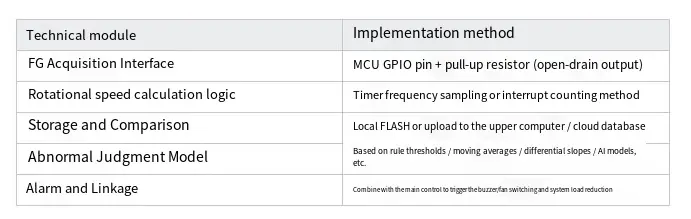
Engineering Realization: What specific technical conditions are required to effectively collect FG signals for intelligent diagnosis?
Conclusion:
The FG signal represents the initial step for the fan to transition from a passive component to an active communicator.
In today's era of widespread smart device deployment, fans should no longer remain as "silent hardware." Instead, they must possess the capabilities of being monitorable, feedback-capable, and diagnosable. The FG signal output serves as the foundational element that equips the fan with a "data-driven language."










