News

How to Select the Optimal Cooling Fan for Communication Servers?
Against the backdrop of continuous advancements in 5G communications, data centers, and edge computing, communication servers are tasked with massive data exchange, low-latency transmission, and critical business processing. To ensure the stable operation of core components such as CPUs, GPUs, and storage units, selecting an appropriate Cooling Fan is of paramount importance.
This article will provide an in-depth analysis of how to choose the optimal fan for communication servers from multiple perspectives, including operational environment, power management, lifespan, and reliability.


What are the key distinctions between air cooling and convective heat dissipation?
In the field of electronic device thermal management, air cooling and convection cooling are two commonly employed heat dissipation techniques.
Air cooling is a method that utilizes airflow generated by fans to remove heat. It typically consists of a heatsink and a fan, where the fan directs air across the fins of the heatsink, transferring heat away from the source (such as a CPU or GPU) and expelling the heated air from the system. Air coolers operate through the synergistic action of metallic heatsinks and fans to reduce temperature. The heatsinks, usually fabricated from materials with high thermal conductivity such as aluminum or copper, efficiently conduct heat away from the source to the fins. The fan enhances airflow across the heatsink surface, thereby accelerating heat dissipation.

How to tell if a cooling fan is working?
To ensure the lifespan and efficiency of your electronic devices, it’s crucial to know how to tell if your cooling fan is working properly. A malfunctioning fan can cause overheating, which can seriously damage your device. Fortunately, there are some simple and effective ways to check if your cooling fan is working properly.


What is a cooling fan used for?
The Role of Cooling Fans in Modern Devices
Cooling fans are essential components in a wide range of products across various industries, ensuring optimal performance and longevity. Technological advancements have driven a surge in demand for efficient cooling solutions, particularly in new energy vehicles, automation, and medical equipment.


What are the extensive applications of cooling fans?
In contemporary life, cooling fans serve not merely as tools for chip temperature regulation, but also perform critical functions in numerous often-overlooked applications. The following highlights unconventional domains where fans operate with quiet indispensability in daily contexts.

How many types of cooling fans are there?

Why is a Fan Essential for High-Density Communication Equipment? A Warm Guide to Thermal Management Logic
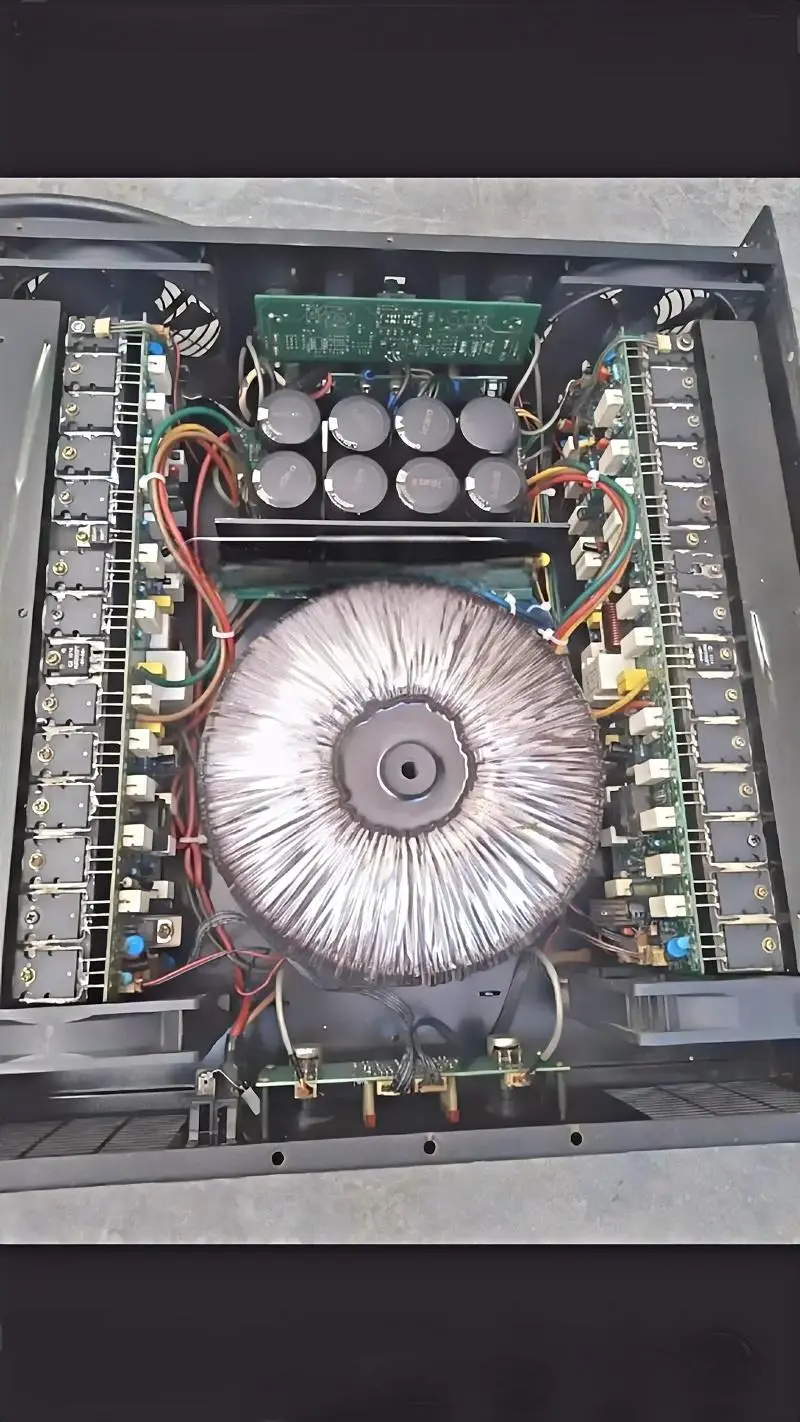
I. Why Do High-Density Communication Devices Generate Significant Heat?
Heat Source Composition
• High-Speed Processors/FPGAs: Intensive computational workloads result in thermal dissipation ranging from 100W to 300W.
• High-Speed Interface Modules (e.g., 400G/800G Optical Modules): Power-hungry driver ICs contribute substantially to heat generation.
• Power Conversion Modules: Thermal losses occur during AC/DC and DC/DC conversion processes.
• RF Modules: Power amplifiers (PAs) typically exhibit only 30–50% energy efficiency.
Power Consumption-to-Heat Dissipation Correlation Table (Approximate Values):
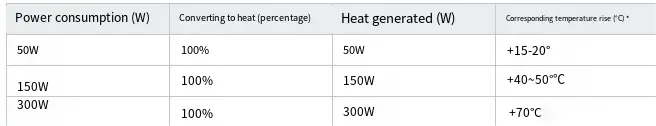
The temperature rise depends on factors such as the heat dissipation structure, air volume, and ambient temperature.
II. Consequences of Omitting Cooling Fans
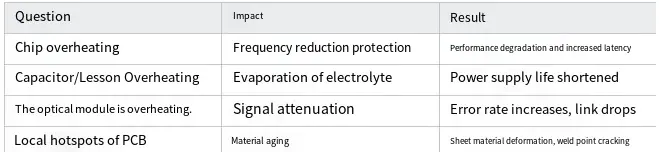
Conclusion: In high-density communication equipment, thermal runaway not only compromises performance but may also result in complete system failure or even irreversible damage.
III. The Pivotal Role of Fans in Thermal Management
✅ Active Cooling: Unlike passive heat sinks, fans proactively facilitate airflow to rapidly dissipate thermal energy.
✅ Precision Temperature Control: Integrated with temperature sensors and PWM speed modulation, fans dynamically adjust airflow based on real-time demand.
✅ Space Efficiency: High-speed fans deliver superior cooling performance within confined spatial constraints.
✅ Enhanced MTBF: By reducing operating temperatures of critical components, each 10°C decrease extends service life approximately twofold (per Arrhenius' Law).
Typical Airflow Requirements for Communication Equipment (Assumed Temperature Rise ≤ 15°C):
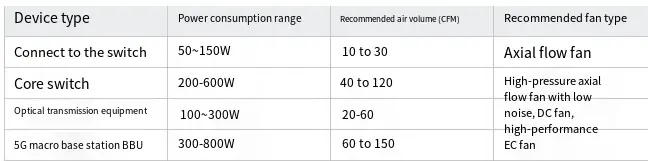
IV. Fan Design Logic for High-Density Communication Equipment
1️⃣ Airflow Path Optimization → Ensures cold air passes through heat-generating components rather than forming short-circuit recirculation
2️⃣ Static Pressure Matching → High-density boards exhibit elevated flow resistance, necessitating high-static-pressure fans (with superior Pa ratings)
3️⃣ Acoustic Performance → Multi-device operation in communication rooms demands low-noise fans (with optimized dBA levels)
4️⃣ Redundancy & Hot-Swap Configuration → Dual-fan or N+1 redundancy design prevents single-point failure scenarios
5️⃣ Intelligent Speed Regulation → PWM/EC-controlled real-time RPM adjustment based on thermal conditions enhances operational longevity and energy efficiency
V. Why do communication devices mostly choose DC/Ec Fans instead of AC ones?
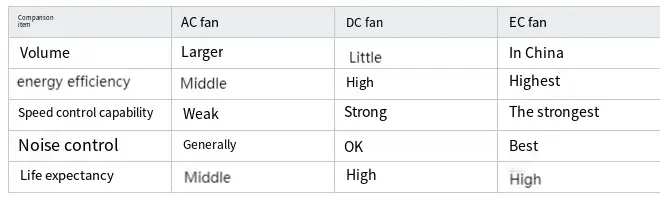
Field experience demonstrates that incorporating PWM speed control with DC/EC fans in communication cabinets effectively reduces noise levels while simultaneously extending the operational lifespan of both the fans and associated equipment.
VI. Communication Thermal Management Solutions by Shenzhen Fuqingda Electronics Technology Co., Ltd.
We provide comprehensive fan selection and thermal management solutions for the telecommunications industry, including:
• High-static-pressure axial fans: Optimized for high-density PCB airflow resistance
• Low-noise DC fans: Ideal for telecommunication equipment rooms
• Energy-efficient EC fans: Delivering 20-40% power savings during prolonged operation
For inquiries regarding these solutions, please contact our team.


How to Choose the Right Cooling Fan: Essential Tips and Guide

How long do cooling fans last?
When it comes to cooling fan lifespan, there are several factors to consider, including the type of bearings used and the operating environment. A key consideration is the cooling fan’s lifespan at a stable indoor temperature (25 degrees Celsius). This temperature is generally ideal for maximizing cooling fan lifespan because it minimizes thermal stress and wear.


What is the best fan to buy?
When choosing the best cooling fan, several key features can significantly enhance your experience. A top-quality cooling fan should provide high airflow, ensuring efficient airflow and keeping your space comfortable. Furthermore, low-noise operation is crucial for maintaining a quiet environment, especially in environments like offices or bedrooms.











