News
Cooling fan structure design principle(2)
3, Fan Structure and Flow Field Analysis:
1,Generation of Fan Airflow
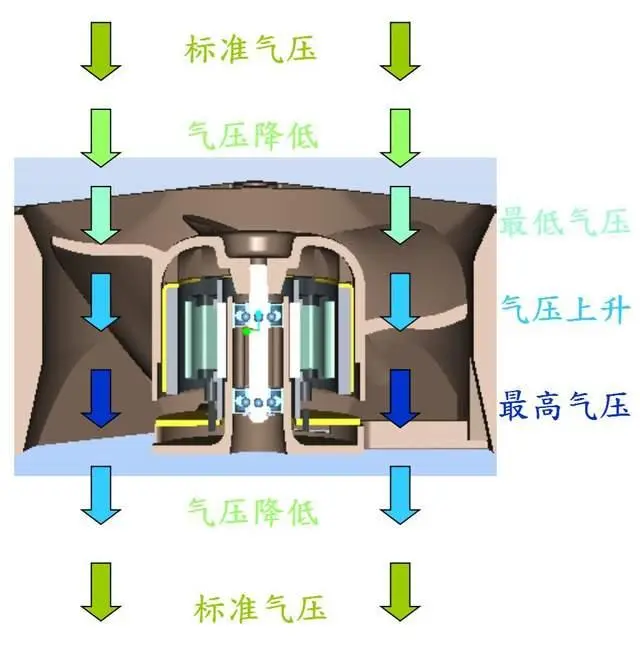
The rotation of the fan blade displaces air particles within its vicinity, causing a decrease in air pressure at the inlet and a corresponding increase in air pressure at the outlet. This results in an axial pressure gradient across the entire fan blade region. Since the external air pressure surrounding the inlet is higher than that inside the inlet, this pressure differential causes external air to be drawn into the system. The incoming air is then transported by the rotating blades towards the high-pressure area, further reducing the air pressure at the inlet. This process continues until the rate of air intake matches the rate of air expulsion from the outlet, establishing a dynamic equilibrium

Cooling fan structure design principle(1)
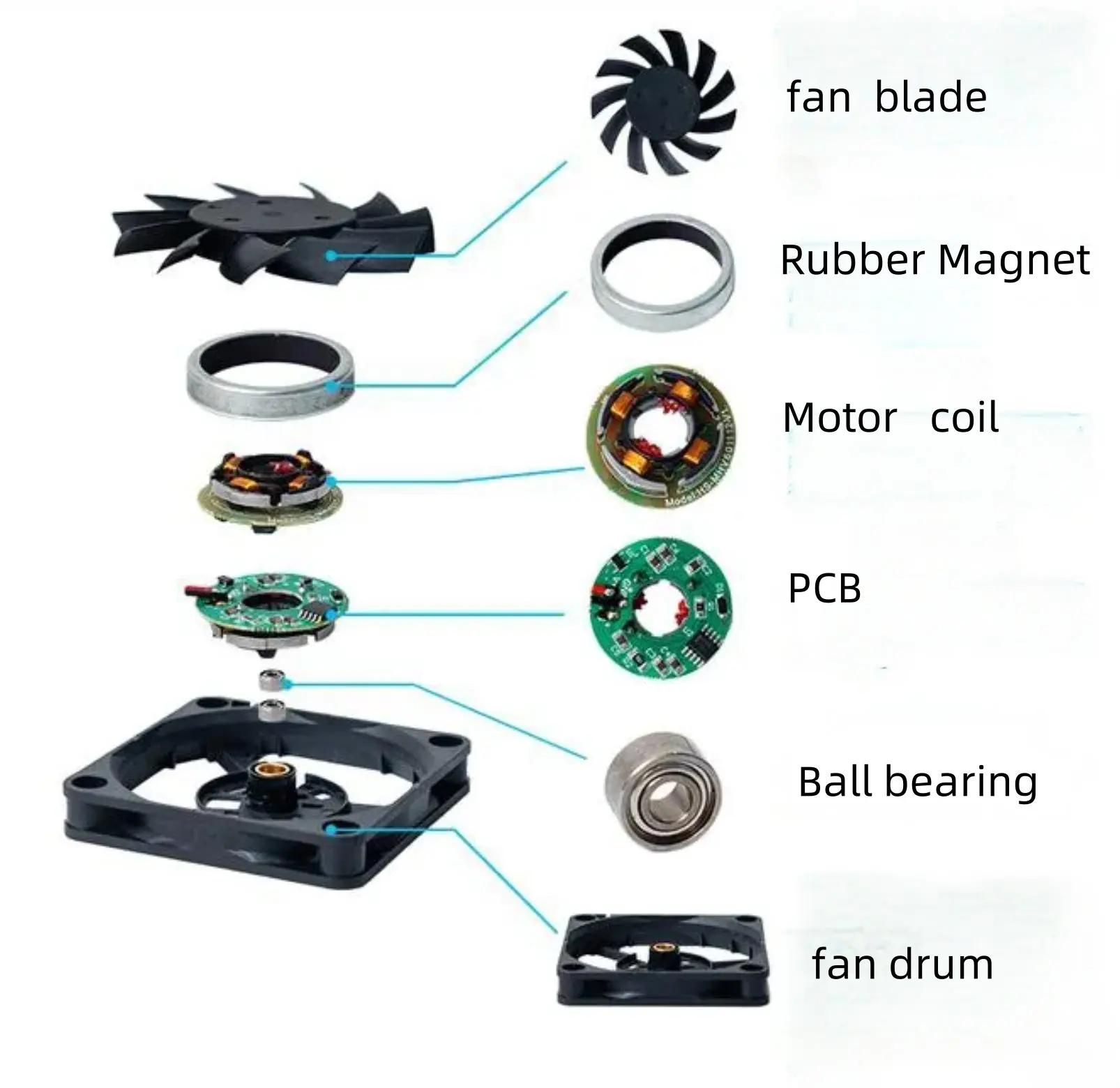
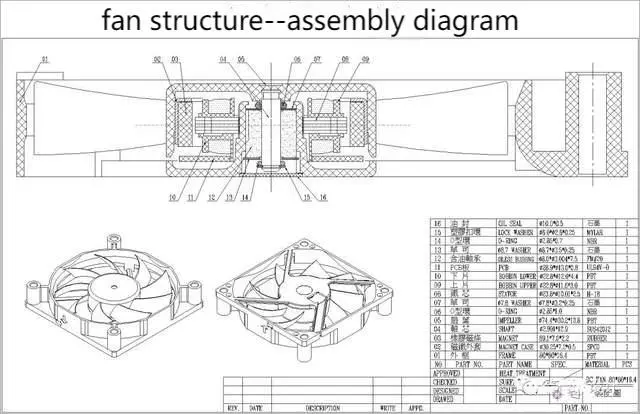
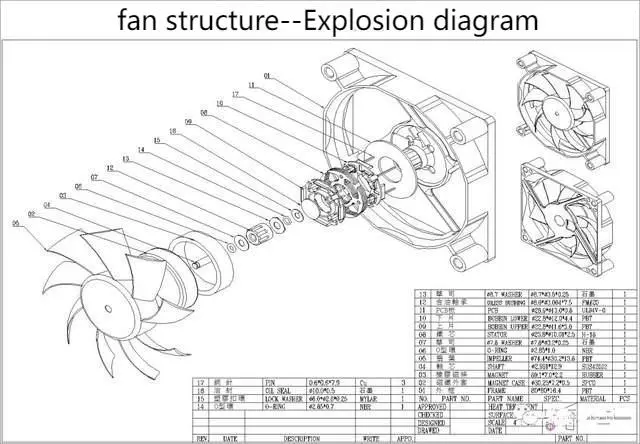
1. The composition and principle of the Cooling Fan
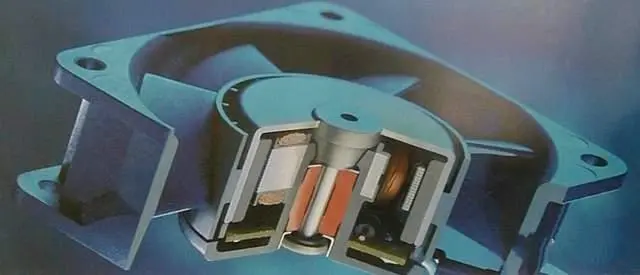
Involve a magnetic rubber ring embedded within the fan blade, which is filled with magnetic material to form a permanent magnet external magnetic field. Two sets of coils wound on the silicon steel sheet are energized, generating a magnetic field. The Hall effect sensor synchronizes the detection and control circuit, enabling alternating operation of the two coil sets on the silicon steel sheet. This results in the silicon steel sheet producing alternating magnetic poles that generate repulsive forces with the magnetic rubber ring. When the repulsive force exceeds the static friction force acting on the fan, the fan blades rotate. Due to the synchronization signal provided by the Hall effect sensor, the blades continue to operate continuously.
2] Factors of fan structure design
Size specifications, appearance requirements
Air pressure Requirements for air volume
Noise requirement
Speed range
Fan output power
Environmental requirements. Functional requirements
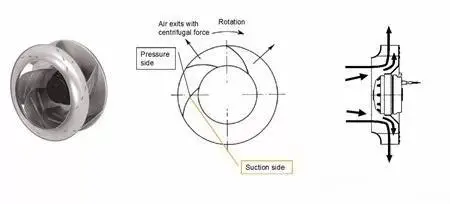
Why choose a centrifugal fan that bends backwards?
When defining the required volumetric flow rate, it is essential to consider the flow resistance encountered by the fan within the application context, as well as its capability to provide fresh air or support a cooling process. The volumetric flow rate (measured in m³/hr) and pressure (measured in Pascals, Pa) are two critical parameters that must be addressed in fan operation. It is crucial to select a fan whose performance characteristics align with these requirements, ideally operating near its peak efficiency point. Utilizing the fan’s peak efficiency not only minimizes energy consumption and noise levels but also ensures optimal performance.
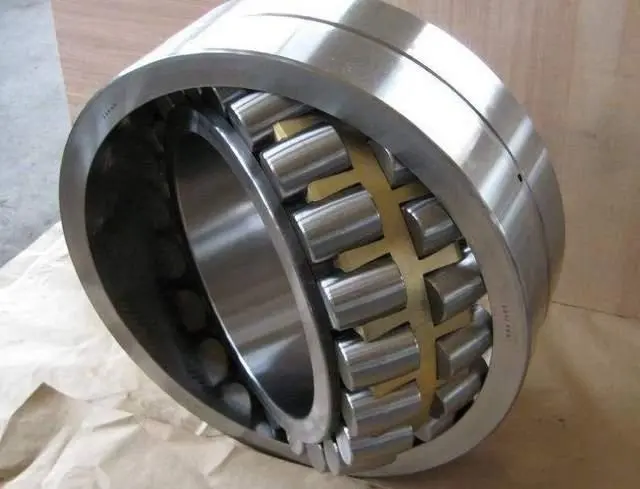

Introduction to different bearings of cooling fan
1. Definition of Bearings:
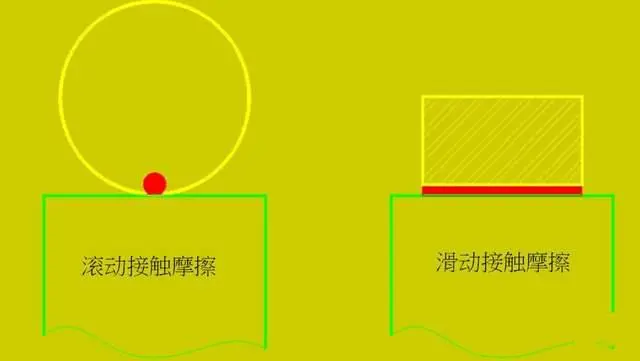
In a broad sense, when two components have relative motion, their interaction can be considered as forming a bearing. Bearings are mechanical components designed to support moving parts, reduce friction, and bear the load of the device. They typically involve surface, line, or point contact with other rotating components, generating friction as these surfaces move relative to each other. The goal is to minimize friction and wear while occupying minimal space and offering cost-effective solutions.
2. Bearings can be classified into two main categories: sliding contact bearings and rolling contact bearings.
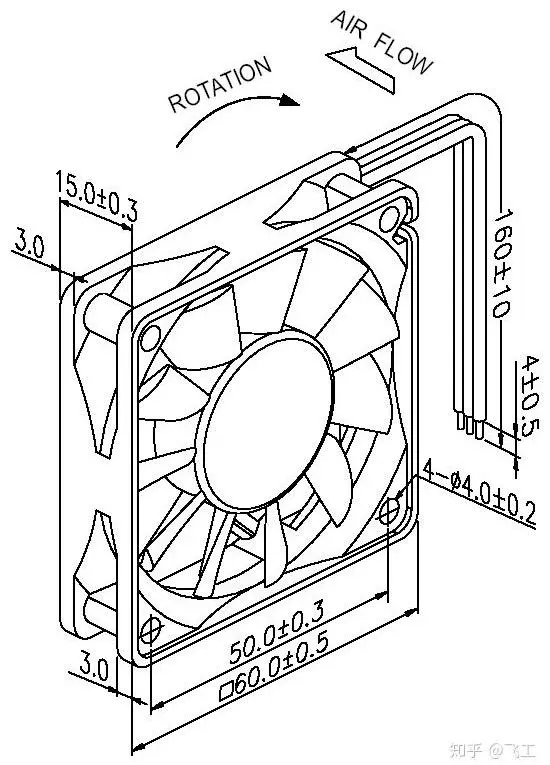
Type and classification of cooling fans
Cooling Fans can be classified as follows:
1. According to the blade type and air flow mode: Axial Fan, centrifugal fan (BLOWER), side fan, oblique fan; When the AXIAL FAN works, the blade pushes the air to flow in the same direction as the shaft, so it is called the axial fan. When the runoff fan works, the blade pushes the air to flow in a direction perpendicular to the axis (that is, radial),
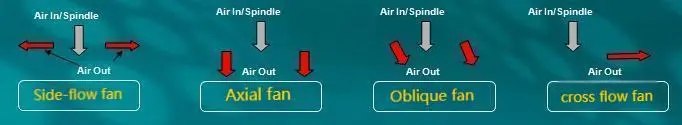
Share the characteristics and features of four cooling fans
The technology and performance of cooling fans have reached a mature stage, and new technologies continue to emerge.
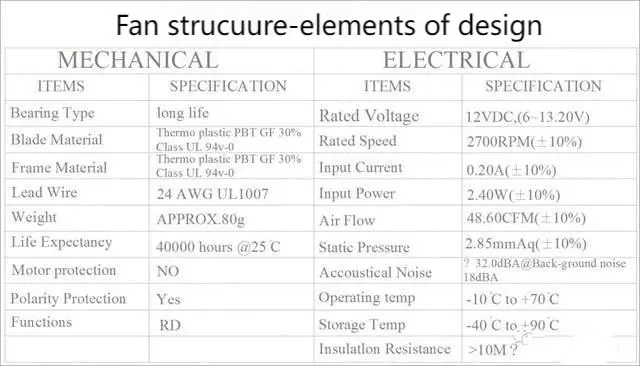
The cooing fan size ranges from 8 mm to 280 mm, and the voltage is 5V, 12V, 24V, 48V, 110V, 220V, 380V, square, round, olive, etc.

Analysis of cooling fan structure and main parameters
"With the continuous progress of science and technology, the more powerful the function of electronic products, the popularity of personal computers, video surveillance, routers, switches and other electronic equipment, the function of the equipment is increasingly powerful, the integration of electronic components is becoming more powerful, the heat and noise generated by electronic components, but let us feel tired, so the heat dissipation of electronic components has become more and more important."
Fan is the use of forced heat convection way of heat dissipation, it relies on its own diversion effect, so that the air at a certain speed, a certain way through the heat sink, using the heat exchange between the air and the heat sink to take away the heat accumulated on it, so as to achieve the "forced convection" heat dissipation method.

Cooling fan bearing introduction: analysis of advantages and disadvantages of different bearings
Different functions and types of cooling fans, the bearings used by the fans are not the same. What are the main bearings of the cooling fan, and what are the advantages and disadvantages of different bearings? The following health electronics to give you a detailed introduction:
The relationship between the air volume and the air pressure of the cooling fan
Cooling fans are typically classified into the following three types:
-
Axial flow type: The direction of the airflow outlet is the same as the axial direction.
-
Centrifugal type: It utilizes the centrifugal force to fling the airflow outward along the blades.
-
Mixed flow type: It incorporates both of the aforementioned airflow patterns.
The principle of cooling fans
Principle: The working principle of a fan is achieved through energy conversion, namely: electrical energy → electromagnetic energy → mechanical energy → kinetic energy. The circuit principle of a fan is generally divided into multiple forms. Different circuits employed will lead to variations in the fan's performance.

Knowledge principle and internal composition of DC brushless cooling fan
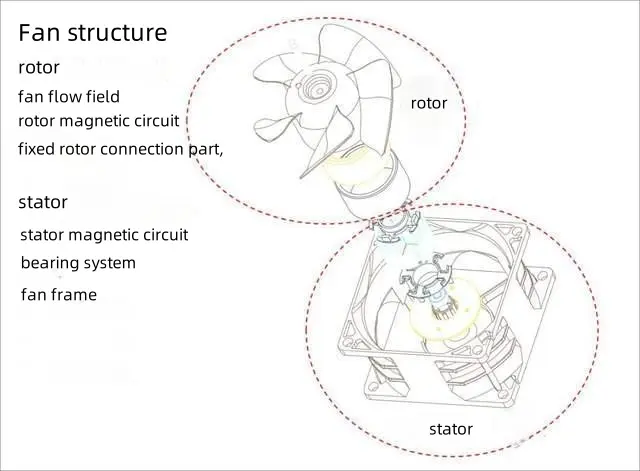
DC brushless fan structure: It can primarily be divided into four major components - the rotor, stator, frame, and motor - along with several other ancillary parts.