News
How to Precisely Choose Cooling Fans?
In modern electronic equipment, the selection of an appropriate Cooling Fan is critical for ensuring the stable and efficient operation of the system. Shenzhen Fuqingda Electronic Technology Co., Ltd., a leading enterprise in the cooling fan industry, boasts an extensive product range and a highly skilled technical team dedicated to providing customers with optimal cooling solutions. Given that the air volume has been predetermined, this article will outline the methodology for accurately selecting a cooling fan to ensure effective heat dissipation.

The Reliability Testing of Cooling Fans and Its Importance
In the domain of electronic equipment cooling, the reliability of cooling fans serves as a critical metric for evaluating their performance and durability. To ensure stable operation across diverse environments and conditions, a comprehensive suite of reliability tests and testing equipment is extensively employed. The following outlines the reliability test procedures for the cooling fans manufactured by Shenzhen Fuqingda Electronic Technology Co., Ltd.


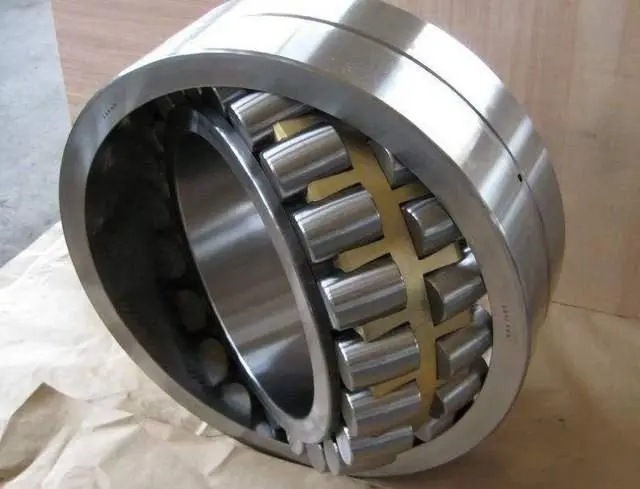
What types of bearings are utilized in high-load, continuously operating cooling fans?
In a high-load server environment, selecting appropriate cooling fan bearings is critical. According to our research and industry experience, two ball bearing fans are undoubtedly the optimal choice.
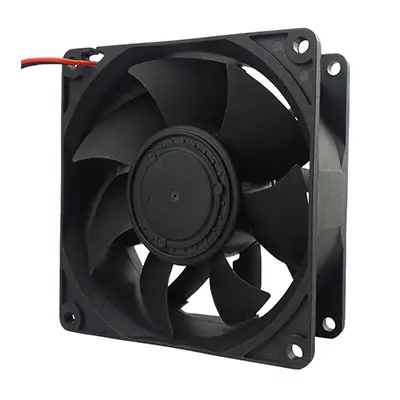


Applicability Analysis of the 17251 and 9238 Cooling Fans for Hydrogen Fuel Cell Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs)
17251 Cooling Fan:
The dimensions are 170mm x 170mm x 51mm, with a typical operating voltage of 24V or 48V. It commonly features dual ball bearings and employs a standard control mode of 4-wire PWM + FG. This model can be equipped with accessories such as a metal mesh guard, power cable, switch wire, speed control wire, and others.

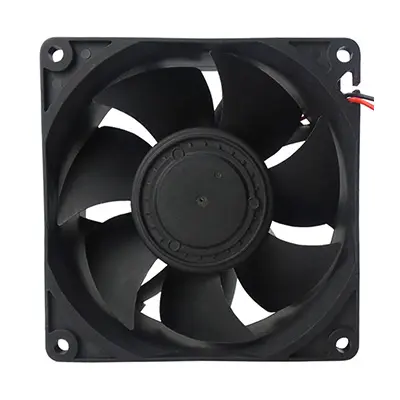
9238 Cooling Fan:
The dimensions are 92mm x 92mm x 38mm, with an operating voltage of 24V or 48V. It typically uses dual ball bearings and is known for its high rotational speed. The standard control mode is 4-wire PWM + FG.

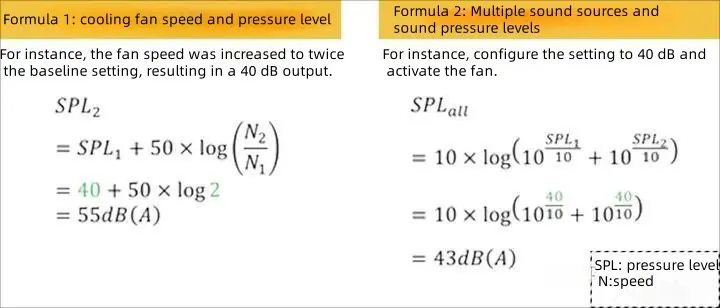
Cooling fan speed and pressure level

Formula 1 can be utilized to characterize the relationship between sound pressure level and fan speed, while Formula 2 can be employed to describe the resultant sound intensity when multiple sound sources are present.
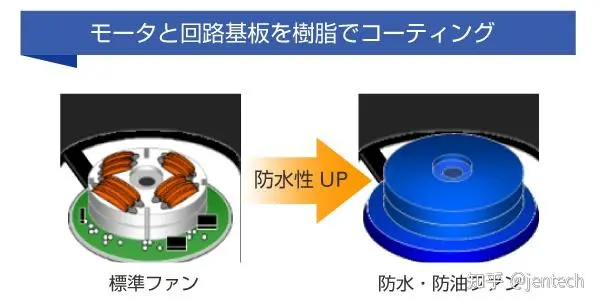
This section outlines the protection ratings for cooling fans.
The IP rating is a standard used to evaluate the dust and water resistance of equipment. The details are as follows:
Definition of IP level:
The IP rating is used to measure the protection of electrical components (such as fans) and electronic components in the equipment against foreign objects (including dust and water).
This rating consists of two numbers, the first number indicating the dust rating (0 to 6) and the second number indicating the water rating (0 to 8).
The specific meaning of IP level:
For example, an IP65 rating indicates that the equipment has "level 6 dust" and "Level 5 water" protection.
Level 6 dustproof means that the equipment is completely dustproof, that is, it is completely protected from dust intrusion.
Class 5 waterproof means that the device is protected against low-pressure water jets from any direction.
Common IP levels:
Depending on the use environment, common IP levels include IP55, IP65, IP67, and IP68.
These grades are typically used for devices that require a specific level of protection.
Standard source:
The IP rating is specified by the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) in the standard IEC 60529.

What are the distinctive features of a counter rotating fan?
The Counter-Rotating Fan is an advanced axial-flow fan that substantially enhances airflow performance and static pressure through the integration of two counter-rotating blade modules within a single fan assembly.
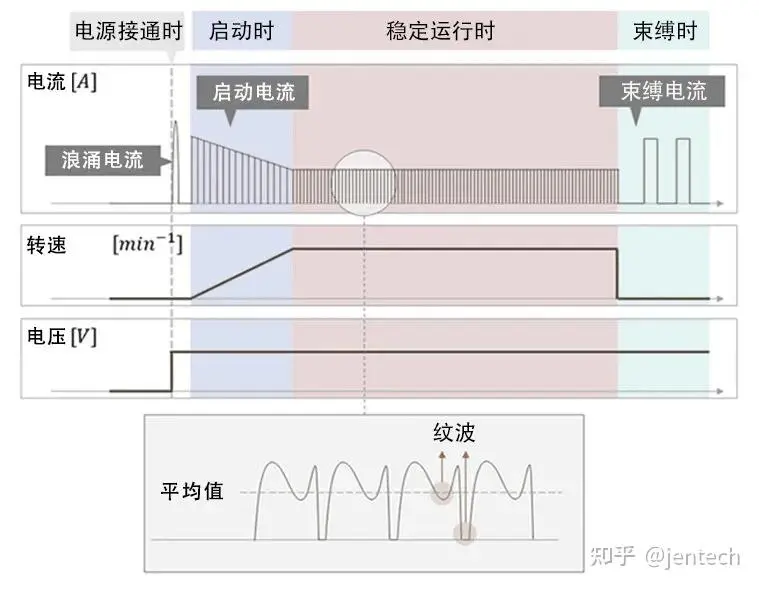
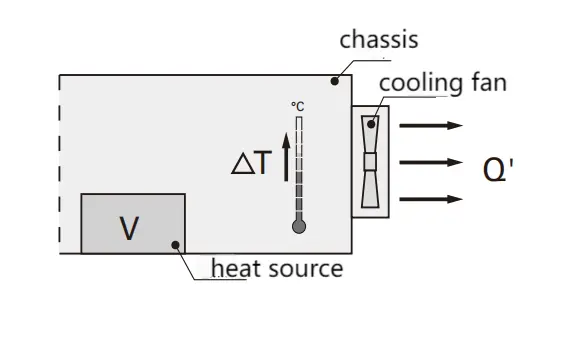
Investigating cooling fan Current Fluctuations: Strategies to Prevent Fan Failure and Prolong Equipment Lifespan
When selecting a cooling fan as a critical component of the equipment, it is essential to consider not only its performance and efficiency but also pay close attention to the characteristics of current variations. Excessive current can lead to fan failure, thereby impacting the normal operation and service life of the equipment. The current variation process of the cooling fan encompasses several stages: the inrush current upon power-on, the starting current during startup, fluctuations in rated current during stable operation, and potential current surges when the fan blades are obstructed. To gain a comprehensive understanding of these current variation characteristics, each stage will be analyzed sequentially to facilitate more informed decisions in cooling fan selection and design.
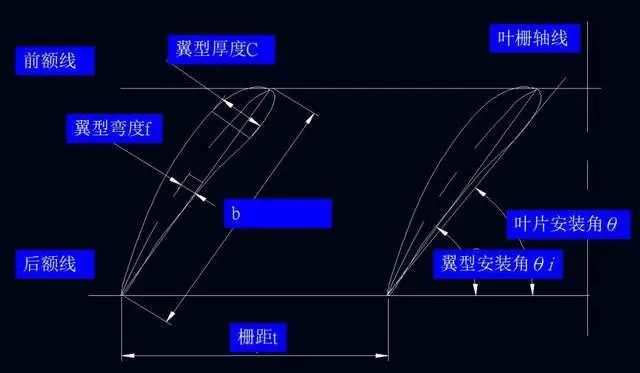
Cooling fan structure design principle(4)
5. Basic equation of fan blade design
The flow in the impeller is very complex, which also causes great difficulties for related research. In order to simplify the difficulty of research, we introduce the following hypothesis for the flow in the impeller, so that the problem is transformed into a unary problem, and a simple equation is derived to describe the characteristics of the machine.
1) The number of blades of the impeller is infinite, and the blades are infinitely thin. Therefore, the flow in the impeller can be regarded as axially symmetric, and the direction of the relative velocity is tangent to the blade surface;
2) The relative flow is steady;
3) The axial velocity is evenly distributed across the flow section.

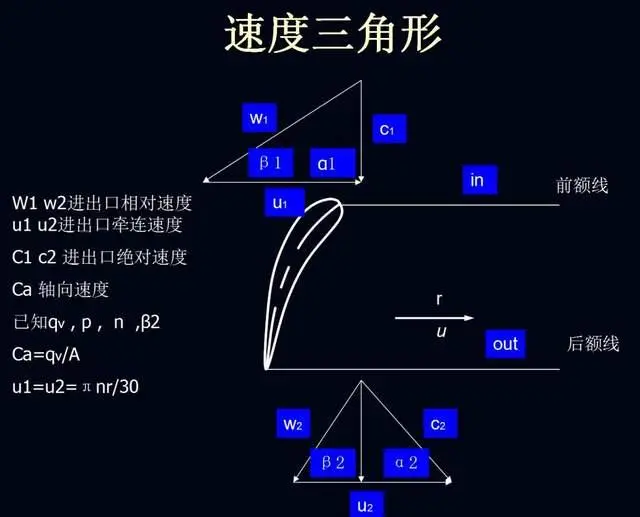
Cooling fan structure design principle(3)
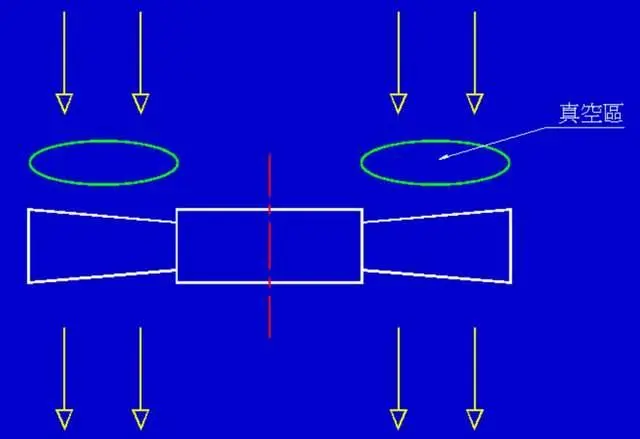
3. Fan Operation Principle
The operation principle of the fan blade is based on Bernoulli's principle. By utilizing the angle of attack (elevation) of the fan blade, a local vacuum is created above the blade when the fan starts. Due to the resulting pressure differential, air is drawn from above the blade and directed downwards, generating airflow. This forced airflow achieves the effect of air supply.