Company News

What are the key distinctions between air cooling and convection cooling?
In the domain of thermal management for electronic devices, air cooling and convection cooling represent two prevalent heat dissipation methodologies.
Air coolingis a heat dissipation technique that employs airflow generated by Fans to remove heat from a system. This method typically comprises a heat sink and a fan, where the fan blows over the heat sink to extract heat from the heat source (e.g., CPU or GPU) and expel it from the system. Air-cooled heat sinks collaborate with metallic heat sinks and fans to reduce temperatures. Heat sinks are commonly fabricated from aluminum or copper due to their high thermal conductivity, enabling efficient heat transfer from the heat source to the heat sink. The fan enhances airflow, facilitating the removal of heat via the heat sink.
Convective heat dissipation refers to a heat transfer mechanism where heat is transferred through the movement of fluids (gases or liquids). In this process, when the surface temperature of an object is elevated, warm air rises and is replaced by descending cooler air, creating a convective cycle. Convective heat dissipation can occur naturally or be forced. Natural convection relies on the buoyancy-driven movement of fluids, where hot air rises and cold air descends, forming a natural circulation. Forced convection utilizes external forces, such as fans or pumps, to drive fluid flow, thereby accelerating heat transfer.
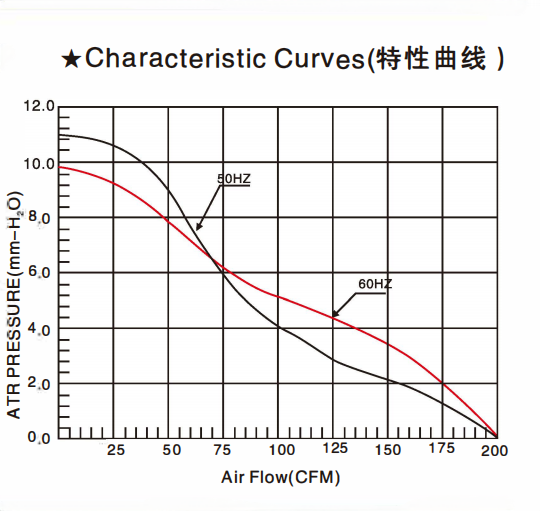
What is the relationship between the ventilation resistance of a cooling fan and its static pressure characteristics?
In the application of Cooling Fans, ventilation resistance and static pressure characteristics are two critical performance indicators that are closely interrelated and significantly influence cooling efficiency. A thorough understanding of their relationship is essential for the proper selection and effective utilization of fans, particularly in scenarios such as high-density equipment heat dissipation, industrial equipment cooling, and applications requiring high-performance air-cooling systems. This paper aims to comprehensively analyze the correlation between ventilation resistance and static pressure characteristics, as well as their implications for the operational performance ofcooling fans.

What are the optimal strategies for arranging the cooling fan to minimize the overall ventilation resistance?
When designing electronic equipment or industrial systems, the layout design of cooling fans plays a critical role. Ventilation resistance is one of the primary factors influencing the efficiency and heat dissipation performance of the fan. Excessive ventilation resistance not only impairs the airflow generated by the fan but also leads to elevated device temperatures, thereby compromising the stability and lifespan of the equipment. This article aims to investigate strategies for optimizing the layout of cooling fans to minimize overall ventilation resistance, thus enhancing cooling efficiency and system performance.

What are the application scenarios for ACDC fans in new energy equipment?
With the growing global focus on sustainable energy, the application of new energy technologies has expanded significantly, encompassing solar power, wind power, electric vehicles (EVs), energy storage systems, and beyond. In these systems, temperature management and heat dissipation are critical factors for optimal performance. ACDC fans, with their superior performance characteristics, have emerged as an essential component in new energy equipment. This article aims to explore the application scenarios of ACDC fans within the realm of new energy technologies and demonstrate how effective thermal management contributes to enhancing equipment efficiency and reliability.

In what way does grease life influence the overall lifespan of the fan?
When selecting and designing industrial cooling systems, it is common to focus on the performance parameters of the fan, such as air volume, speed, and static pressure. However, it is important to recognize that the Grease Life of the fan serves as a critical factor that ultimately determines its overall service life.
✅ What is grease life?
Grease life refers to the duration during which the lubricating grease within the fan's internal bearing can maintain effective lubrication. Once the grease degrades, the bearing will experience increased wear, leading to unstable fan operation, elevated noise levels, and potentially even seizing or complete failure. For fans utilizing ball bearings, grease degradation represents the most critical factor limiting their lifespan.
Fan life ≒ bearing life ≒ grease life
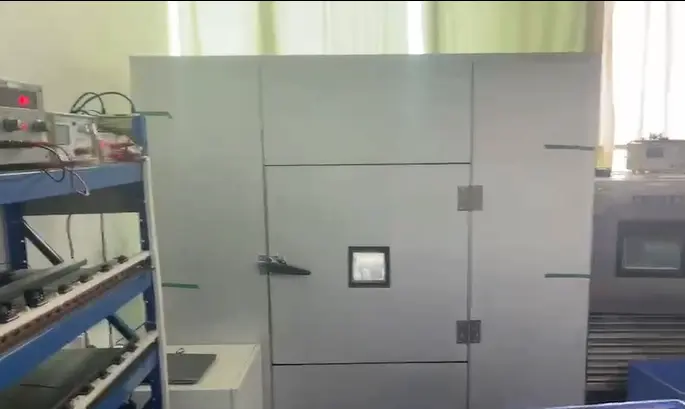

In what ways does vibration testing contribute to the extended lifespan of cooling fans?
Vibration testing serves as a critical method for assessing the durability and lifespan of cooling fans. By conducting systematic vibration analyses, fan manufacturers can refine their designs, choose more appropriate materials, and enhance production processes to develop fans that are both reliable and long-lasting. When selecting a cooling fan, users should consider its vibration performance, particularly for equipment operating under high loads or in harsh conditions.
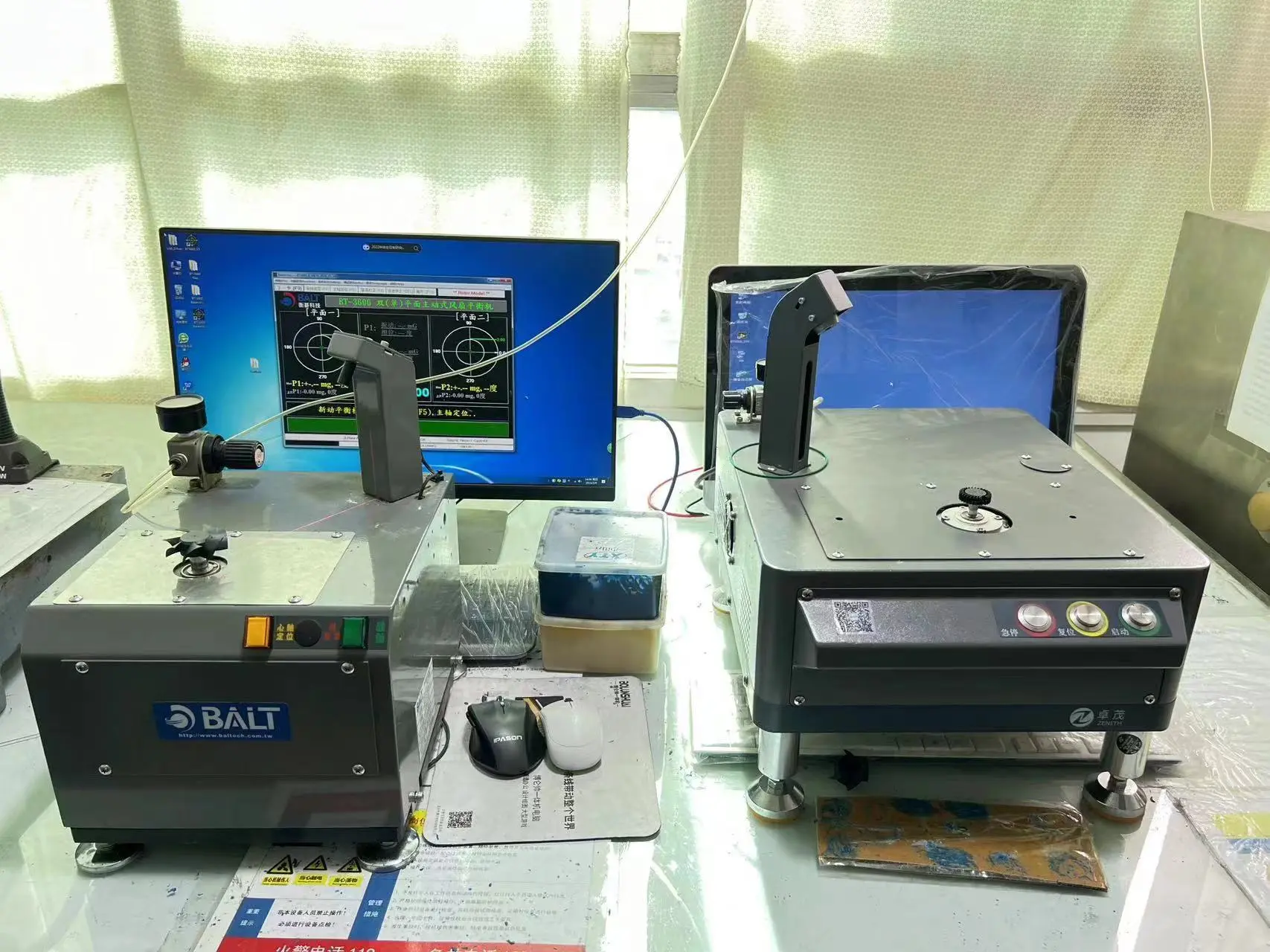

What is the correlation between the lifespan of cooling fans and vibration testing?
In modern electronic equipment, cooling fans play a critical role. They not only effectively reduce the temperature of the equipment but also ensure its stable operation under high loads. However, the service life of the fan is influenced by several factors, among which vibration is particularly significant. The vibration generated during the fan's operation directly affects its lifespan. Understanding the relationship between vibration and fan life can facilitate the optimization of fan design and usage, thereby enhancing the overall reliability of the equipment.
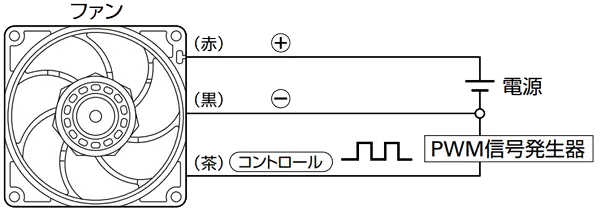
Why is it necessary to use PWM cooling fans in conjunction with temperature sensors?
In modern electronic devices, the challenge of heat dissipation has consistently been a critical issue. As equipment performance continues to improve, the demand for efficient heat dissipation is increasing. Fans, as one of the key solutions for heat dissipation, play an essential role in these devices. PWM (pulse width modulation) control technology has been extensively adopted in fan control systems to dynamically adjust fan speed in response to equipment temperature changes, thereby optimizing heat dissipation efficiency. However, to achieve optimal performance, PWM fans typically require integration with temperature sensors. This article explores why PWM cooling fans necessitate the use of temperature sensors.

What is the rationale behind establishing a minimum and maximum operating temperature limit for the cooling fan?
Cooling fans are an essential component of electronic devices, as they dissipate heat through air movement to ensure the normal operation of the device. Nevertheless, the operating temperature range of cooling fans is not unlimited; instead, it is bounded by specific minimum and maximum thresholds. Below are several factors contributing to these limitations and their potential effects on device performance.

How to Select the Optimal Cooling Fan for LED Lamps?
With the widespread adoption of LED lamps across various lighting applications, there is growing attention being paid to the heat dissipation challenges associated with these lamps. While LED lamps are renowned for their long service life and high luminous efficiency, excessive heat accumulation over extended periods can degrade performance and reduce lifespan. Consequently, selecting an appropriate cooling solution becomes crucial. This article aims to guide you in choosing the ideal cooling fan tailored to the specific requirements of LED lamps by considering multiple factors.









